RAM
(Random Access
Memory)
The
most common type of memory is called random access memory (RAM). As a result,
the term memory is typically used to mean RAM. RAM is like an electronic
scratch pad inside the computer.RAM holds data and program instructions while
the CPU works with them. When a program launched, it is loaded into and run
from memory. As the program needs data, it is loaded into memory for fast
access. As new data is entered into the computer, it is also stored in memory
but only temporarily.
SIMM 30 Pins (Use in
8086--------------------------80586 computers)
SIMM 72 Pins (Use in
80386--------------------Pentium II computers)
DIMM or SD Ram (168 pins) (Use in Pentium I---------------Pentium
IV computers)
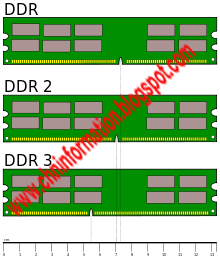
DDR I (184 Pins) (Use in Pentium IV
computers)
DDR II (240 Pins) (Use in Pentium IV
computers)
DDR III (200/240 Pins) (Use in Pentium IV Advanced computers)
RD (184 Pins) (Use
in Pentium IV computers)
SIMM = Single inline Memory Module
DIMM = Dual inline Memory Module
RD = Rambus Dynamic Random Access Memory
SD = Static Dynamic or Standard Dynamic
DDR = Double Data Rate or Double Data Raw
DIMM = Dual inline Memory Module
RD = Rambus Dynamic Random Access Memory
SD = Static Dynamic or Standard Dynamic
DDR = Double Data Rate or Double Data Raw















0 comments:
Post a Comment